
|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
In the world of Digital Marketing, efficient sales strategies play a crucial role in the success of any business. Two notable approaches in this context are the flywheel and the sales funnel. In this article, we'll explore the differences between these models and discuss how to integrate them to drive results.
Flywheel and sales funnel concept
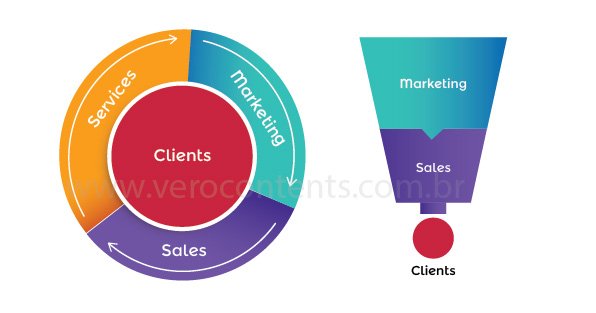
The sales funnel is a traditional structure that represents the steps a customer goes through, from discovering the product to making the purchase. In this way, it is a representative model of the steps that a potential customer goes through from the first contact with a company to the completion of the purchase. This concept is often used in the context of marketing and sales to visualize and understand the process of converting leads (potential customers) into actual customers. The sales funnel is called this because of its shape that resembles a funnel, where the width represents the initial phase of the process and the narrow part represents the conclusion of the sale.
In contrast, the flywheel is a newer approach, emphasizing customer satisfaction and the continuous generation of positive energy. The flywheel model in inbound marketing it is a strategic approach. In this way, it focuses on creating a continuous cycle of customer attraction, engagement and satisfaction to drive sustainable growth of a company. This concept is an alternative to the traditional sales funnel model, highlighting the importance of placing the customer at the center of marketing and sales strategies. And more than that, it serves as a complement to the funnel concept, and can be applied together.
The “flywheel” metaphor represents the idea of a rotating disc that accumulates energy over time. Thus, this energy is generated by satisfied and engaged customers, fueling a positive cycle of growth. The flywheel is based on the principles of attracting, engaging and delighting customers to create a solid and lasting foundation.
Importance of efficiency in sales processes
Efficiency in sales processes is vital to the success of any company. Therefore, understanding how the sales funnel and flywheel differ and how they can work together is essential to optimizing sales strategies.
Efficient processes allow sales teams to focus on the most impactful activities, increasing productivity and reducing wasted resources. Additionally, they ensure teams are approaching the right leads, which leads to improved sales quality and customer satisfaction.
Combining the sales funnel, focused on traditional acquisition stages, with the flywheel, focused on customer satisfaction, ensures a comprehensive customer-centric approach throughout the entire sales cycle.
Understanding the sales funnel
The sales funnel represents a linear process, divided into three phases: top, middle and bottom. Each phase has specific goals, from attracting initial attention to converting leads into customers.
Traditional funnel stages
Top of the Funnel (ToFu): At this stage, marketing efforts aim to attract the attention of a wider audience. In this way, the objective is to generate awareness about the brand, products or services. Strategies include creating relevant content, social media presence, advertising and other tactics to attract potential interested parties.
Middle of the Funnel (MoFu): Here, leads are more engaged and have shown interest in exploring more about the company. Therefore, the focus is to educate these leads by providing more detailed information, product demonstrations, case studies, webinars and other resources that help with decision making.
Bottom of the Funnel (BoFu): In the final phase, leads are more likely to become customers. Thus, strategies focus on closing deals, offering commercial proposals, more detailed demonstrations, customer testimonials and other forms of incentives for conversion.
Each phase requires specific activities, from creating attractive content to personalized monitoring in the final stage of the sales process.
Getting to know the flywheel
The flywheel is an approach that puts customer satisfaction at the center of sales strategies. In this way, it represents a continuous cycle, where the positive energy generated by customers drives business growth.
Unlike the sales funnel, the flywheel highlights the importance of providing an exceptional customer experience by encouraging loyalty and positive word of mouth.
The main elements of the flywheel model are:
Attract: The process begins by attracting qualified visitors to your company website through content marketing strategies, SEO, social media, and other tactics that spark genuine interest.
Engage: Once visitors are on the website, the next step is to engage them in a meaningful way. This involves providing relevant content, personalized interactions, and positive experiences to turn visitors into leads.
Enchant (Delight): The enchantment phase is crucial for creating brand advocates. Offering exceptional customer support, personalizing interactions, providing memorable experiences and constantly striving for customer satisfaction are essential elements of this stage.
Fundamental differences in relation to the sales funnel
The flywheel breaks the linearity of the sales funnel, promoting a continuous feedback cycle and constant adjustments. While the sales funnel prioritizes closing deals, the flywheel highlights the importance of building lasting, positive relationships with customers.
In this way, the linearity of the sales funnel contrasts with the continuous nature of the flywheel, where customer satisfaction fuels a cycle of constant growth.
The difference with the flywheel is that, instead of considering the customer as the last stage of the process, they are placed at the center of the model, generating positive energy as they progress through the phases. Thus, the flywheel creates a continuous cycle of growth, where satisfied customers become brand promoters, attracting new customers and feeding the flywheel.
Unlike the sales funnel, the flywheel model does not have a single direction. He suggests that marketing and sales are not just about acquisition, but also about maintaining and continually cultivating customer relationships.
flywheel values customer feedback as an essential tool for driving continuous improvements and enhancing the overall experience.
Advantages and challenges of each model
The sales funnel offers a clear structure, making it easy to track progress and identify areas for improvement. On the other hand, the flywheel excels at creating a loyal customer base, driving organic growth and reducing dependence on aggressive acquisition strategies.
As such, both models present challenges, from the need to optimize efficiency in the sales funnel to the requirement to maintain high standards of customer satisfaction in the flywheel.
Model integration: how to do it
Identifying where models overlap is essential for the success of sales processes. Effective integrations occur at transitions between phases of the sales funnel and at opportunities to generate positive energy in the flywheel.
Therefore, communication and collaboration between these areas are crucial to align strategies and ensure a smooth transition between models.
The use of marketing automation, the use of analytical tools and personalized strategies to synchronize models, taking advantage of the best of each approach, is the backbone of successful integration. Inbound marketing and inbound sales go hand in hand in these processes, strengthening results, focusing on the customer and their purchasing journey.
The importance of lead tracking
Lead tracking is an essential practice to effectively integrate the flywheel and marketing funnel into an inbound marketing strategy. Lead tracking refers to the process of monitoring and recording lead interactions (potential customers) throughout the sales cycle. In this way, this monitoring is carried out to obtain insights into the behavior of leads, understand their needs and personalize marketing and sales interactions according to their actions and interests.
Therefore, you must identify the integration points between the flywheel and the marketing funnel, including points such as lead attraction, conversion, closing sales and customer delight.
How to implement lead tracking
To implement lead tracking, use marketing automation tools, such as RD Station e Hubspot, to track lead behavior at every stage of the funnel and flywheel. This includes interactions on the website, opening emails, participating in webinars, among others.
Establish clear criteria to qualify leads based on their interactions. For example, a lead who participates in a webinar may be considered more engaged than one who just downloaded an eBook.
Use the information collected to personalize your approach to leads at different stages of the funnel and flywheel. This could include sending specific content, personalized offers, or invitations to exclusive events.
Integrate your system CRM with marketing automation tools to ensure a holistic view of the customer. This allows for effective collaboration between marketing, sales and customer service teams.
Regularly monitor lead tracking results. Therefore, analyze metrics such as conversion rates, sales cycle time and customer satisfaction. Adjust your strategies based on the insights you gain.
Use lead tracking to identify opportunities for customer delight. Offer proactive support, provide relevant post-sale content, and solicit feedback to continually improve the customer experience.
In short…
By understanding the differences between the sales funnel and the flywheel and exploring efficient integration strategies, companies can position themselves to win customers in a sustainable way, promoting constant growth and lasting satisfaction. Try combining the best of both worlds to take your sales strategies to the next level.
Use marketing automation and lead tracking to foster and monitor your customers’ activities. But don't forget, always prioritize understanding your needs and align teams to keep the flywheel spinning with the aim of delighting and retaining your customers!

Marcel Castilho is a specialist in digital marketing, neuromarketing, neuroscience, mindfulness and positive psychology. In addition to being an advertiser, he also has a Master's degree in Neurolinguistic Programming. He is the founder and owner of Vero Comunicação and also the digital agency Vero Contents.



